Fig. 1
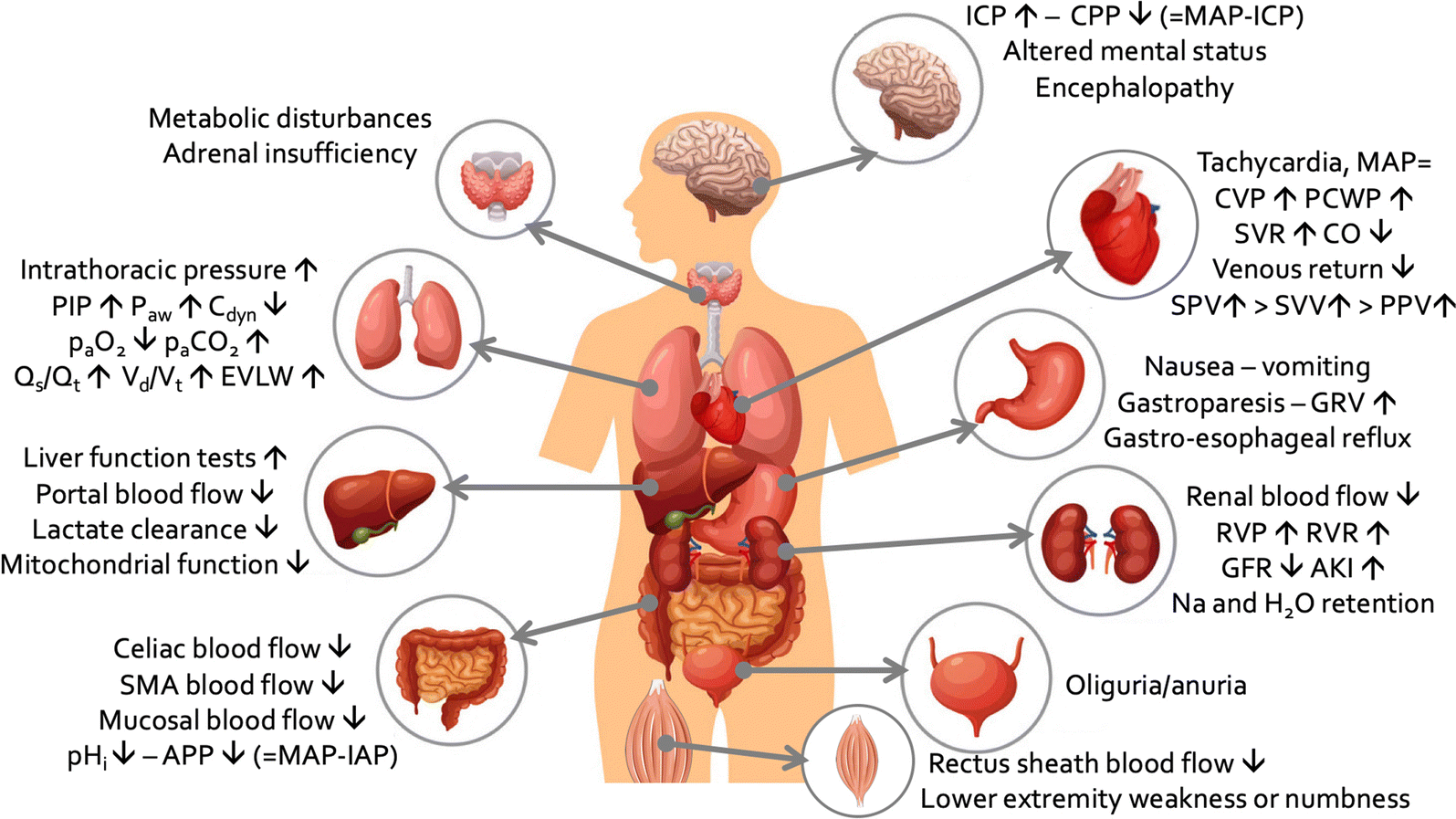
Adapted from Malbrain et al. with permission [126]
Summary of the most important pathophysiologic effects of increased intra-abdominal pressure on end-organ function within and outside the abdominal cavity. AKI acute kidney injury, APP abdominal perfusion pressure, Cdyn dynamic respiratory compliance, CO cardiac output, CPP cerebral perfusion pressure, CVP central venous pressure, EVLW extravascular lung water, GFR glomerular filtration rate, GRV gastric residual volume, HR heart rate, IAP intra-abdominal pressure, ICP intra-cranial pressure, ITP intra-thoracic pressure, MAP mean arterial pressure, PIP peak inspiratory pressure, Paw airway pressures, PCWP pulmonary capillary wedge pressure, pHi intra-mucosal gastric pH, PPV pulse pressure variation, Qs/Qt shunt fraction, RVP renal venous pressure, RVR renal vascular resistance, SMA superior mesenteric artery, SPV systolic pressure variation, SVR systemic vascular resistance, SVV stroke volume variation, Vd/Vt dead-space ventilation.